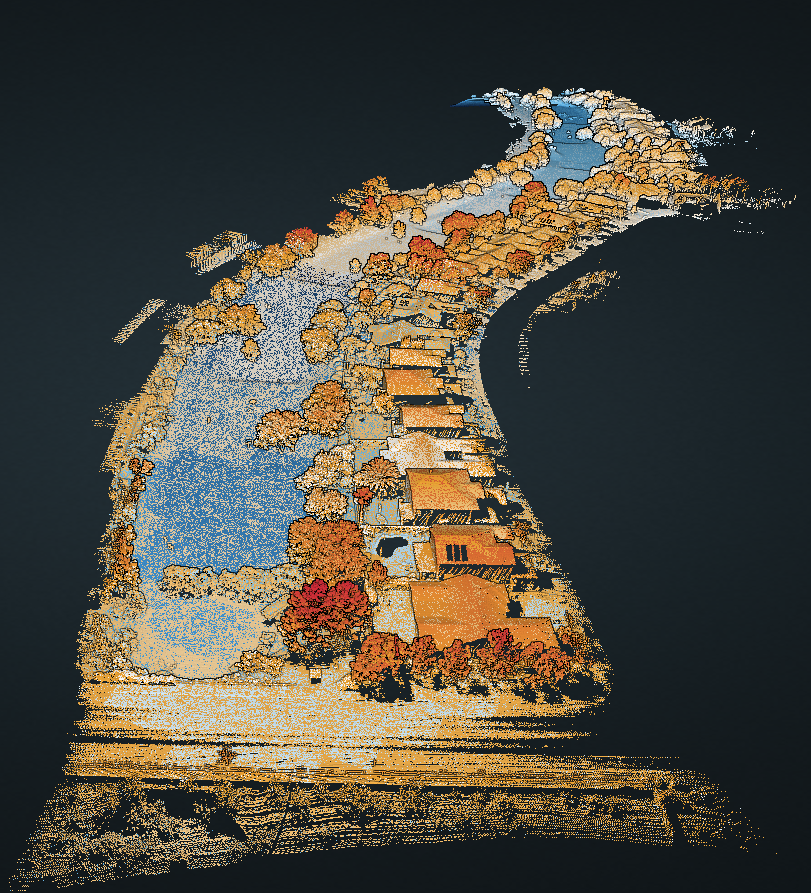
WHAT IS A DEM (DIGITAL ELEVATION MODEL)?
A Digital Elevation Model (DEM) is a representation of the bare ground (bare earth) topographic surface of the Earth excluding trees, buildings, and any other surface objects. DEMs are created from a variety of sources. In the past, USGS DEMs used to be derived primarily from topographic maps.
They are raster grids of the Earth’s surface referenced to the vertical datum—the surface of zero elevation to which heights are referred to by scientists, insurers, land developers, designers, and geodesists.
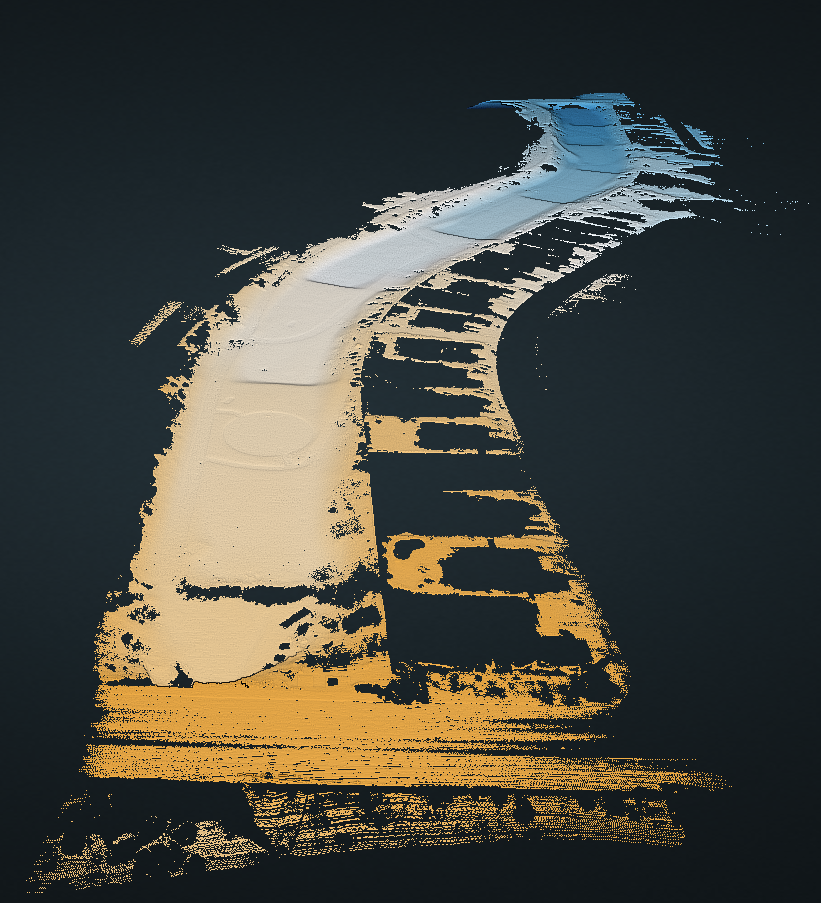
These may be output as TIN (Triangulated Irregular Network) for space-saving/file sizes, while most users prefer to receive full resolution elevation point clouds as viewed to the right.
WHO NEEDS DEM’s?
1. Surveyors
DEM is frequently used to display conventional topographic data of a particular region. Soil mapping and geological studies can also be done using DEM.
2. Cut-and-fill calculations
Earthwork calculations, especially for roads or railroads, can be done using DEM and the ArcGIS software. Calculate fill or haul-off well in advance.
3. Risk assessments
Seismic surveys may be created using DEM. The rock structure will give insights on threats such as landslides and earthquakes. Flood management may also be assessed after a thorough study of the topography.
4. Site planning
Topography and slope analysis aid in planning the site layout. The planning considers underground utilities. DEM provides accurate data for planning.
5. Urban planning
Architects and engineers plan residents/users visibility of a proposed building, taking into consideration the surrounding aspects.
6. Water resources management
Contours, elevation points, and catchment area details of a water body are attained from DEM. Volumetric calculations regarding flow accumulation and flow direction for building reservoirs and dams may be performed.